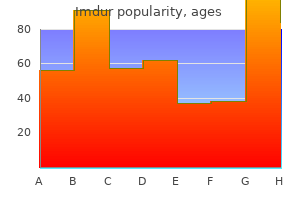
"Purchase generic imdur pills, pain management for my dog".
By: D. Jesper, M.B.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, New York University Long Island School of Medicine
This delusion usually focuses on romantic or spiritual union rather than sexual attraction pain treatment with acupuncture order discount imdur line. It is common for people with erotomania to try to contact the person who is the object of their delusion allied pain treatment center ohio cheap imdur express. The belief that the patient has a great (but unrecognized) ability treatment for nerve pain in dogs buy imdur 40 mg online, talent pain medication for dogs with liver problems cheap 40 mg imdur fast delivery, or achievement. The belief that the patient is being spied on, drugged, harassed, or otherwise conspired against. People with this delusion sometimes become violent against those whom they perceive as harming them. Schizophreniform disorder the psychotic disorder characterized by symptoms that meet all the criteria for schizophrenia except that the symptoms have been present for only 16 months and daily functioning may or may not have declined over that period of time. Brief psychotic disorder the psychotic disorder characterized by the sudden onset of positive or disorganized symptoms that last between a day and a month and are followed by a full recovery. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders 5 3 1 Jeff Kravitz/FilmMagic/Getty Images Diana Napolis suffered from persecutory delusions about filmmaker Stephen Spielberg and singer and actress Jennifer Love Hewitt; she believed that both were controlling her brain (Soto, 2003). The false belief that the patient is experiencing bodily sensations (such as insects on the skin) or bodily malfunctions (such as a foul odor coming from a body cavity). The patient is likely to confront his or her partner with the "evidence" and may try to "prevent" further unfaithful acts by following or attacking the partner. People with delusional disorder-like those with the paranoid subtype of schizophrenia-may appear normal when they are not talking about their delusions: Their behavior may not be particularly odd nor their functioning otherwise impaired. For some, the delusions may ebb and flow, sometimes interfering with daily life and sometimes fading into the background and not having any effect; for others, the delusions may dwindle away and not reappear. Shared Psychotic Disorder Have you ever worried about "catching" a psychological disorder? Perhaps the most exotic psychotic disorder is shared psychotic disorder (or folie а deux, which is French for "paired madness"), which occurs when an individual develops delusions as a result of his or her close relationship with another person who has delusions as Brian To/FilmMagic/Getty Images Shared psychotic disorder the psychotic disorder in which an individual develops delusions as a result of his or her close relationship with another person who has delusions as part of a psychotic disorder; also known as folie а deux. Although diagnosing Barzee was difficult, some doctors who examined her believed that she had shared psychotic disorder. The person who had the disorder at the outset is referred to as the primary person and is usually diagnosed with schizophrenia or delusional disorder. The individual diagnosed with shared psychotic disorder comes to adopt the delusions of his or her close friend or family member. The delusions of the primary person may be shared by more than one other person, as can occur in families when the primary person is a parent. For example, in one case of shared psychotic disorder, the primary person was a young woman with hallucinations and delusions; she was later diagnosed with schizophrenia. She lived with her two older sisters and convinced them that God was talking to her and that they should join her in taking over a nearby house because God wished it. Her sisters came to share the delusions; they attempted to burglarize the house but were arrested. When the older sisters were separated from their ill sister, their delusions abated (Joshi, Frierson, & Gunter, 2006). Although schizotypal personality disorder is not technically a psychotic disorder, we mention it here because some research suggests that it may in fact be a milder form of schizophrenia (Dickey, McCarley, & Shenton, 2002). With this personality disorder, problems in relationships may become evident in early adulthood, marked by discomfort when relating to others as well as by being stiff or inappropriate in relationships. However, before you start to become concerned for yourself or someone you know, keep in mind that relationship difficulties are not enough for a diagnosis of schizotypal personality disorder; eccentric behavior, such as having unusual mannerisms or difficulty following social conventions, must also be present. Schizotypal personality disorder, unlike schizophrenia, does not involve psychotic symptoms. Schizophrenia Facts in Detail In this section we will discuss additional facts about schizophrenia-how common it is, the disorders that are most frequently comorbid with it, gender and cultural factors related to the disorder, and the prognosis for patients with the disorder. Prevalence the world over-from China or Finland to the United States or New Guinea- approximately 1% of the population will develop schizophrenia at some point in their lives (Gottesman, 1991; Perдlд et al. Although schizotypal personality disorder is not a psychotic disorder (because hallucinations and delusions are absent), this personality disorder is considered to be on the spectrum of schizophrenia-related disorders.
Vaccination during Pregnancy Pregnancy should be avoided for 1 month after rubella vaccination best pain medication for a uti cheapest generic imdur uk, but if a pregnant woman is inadvertently vaccinated there is no indication for therapeutic abortion (Department of Health pain medication for nursing dogs imdur 20mg overnight delivery, 1996; Centers for Disease Control pocono pain treatment center purchase imdur 20mg visa, 2001b) pain treatment meridian ms purchase imdur in united states online. Follow-up studies on women who elected to go to term following inadvertent vaccination during pregnancy, or within 3 months before conception, revealed no abnormalities compatible with congenital rubella among 684 babies delivered by these women. The aim of these programmes is to prevent women acquiring rubella while they are pregnant. Data from Germany: IgM positive in 6/126 cord bloods tested with information on health at birth and telephonic information on health at birth in 131 cases. However, as a number of rubella outbreaks occurred among adolescents and young adults in the late 1970s, further emphasis was placed on vaccinating susceptibles in these older age groups, which resulted in a further decline in rubella notifications. This was the result of missed opportunities for rubella screening or vaccination; many of the cases of maternal rubella could have been prevented if postpartum immunisation had been carried out following previous pregnancies. The selective vaccination programme was replaced by universal immunisation of children in 1988, since some of the remaining susceptible pregnant women (23%) were infected during outbreaks as rubella continued to circulate among children. In order to eliminate rubella, it is necessary to monitor the efficacy of rubella vaccination programmes. All countries undertaking rubella elimination should ensure that women of childbearing age are immune and that routine coverage in children is sustained at 80% or above 2. Countries that currently include rubella in their childhood immunisation programmes should ensure that women of childbearing age are immune and should move towards rubella elimination 3. If a global measles eradication goal is established, rubella should be included 4. Rubella vaccine should be considered as a priority for initiatives to introduce new or under-utilised vaccines in developing countries Reproduced by permission of the World Health Organization from Hinman et al. This emphasises the importance of questioning women who come from developing countries when pregnant, about any illness experienced in early pregnancy, so that appropriate tests can be carried out (Department of Health, 2003). This has resulted in measles outbreaks in 2002 and 2003 and may put unvaccinated girls at risk of rubella in the future. Developing Countries Rubella vaccination strategies are unsatisfactory in many developing countries (Robertson et al. It was emphasised that, in order to be effective, programmes Other European Countries Initially selective vaccination programmes were adopted in other countries in Western Europe. By 2002 rubella vaccination was included in national immunisation programmes of 123 (57%) countries/territories, an increase of 14% since 1996 (Figure 12. This has been combined with immunisation of adult females or males and females in some countries, in order to avoid shifting the age of infection to susceptible adults (World Health Organization, 2003b). Caution must be expressed about the introduction of rubella vaccination in countries with relatively low measles uptake rates. It is now recognised that children of both sexes and susceptible adult women should be vaccinated in order to eliminate rubella and avoid an increase in incidence of congenital rubella. Passive Immunisation Women who come into contact with rubella and for whom a termination would be unacceptable may be offered normal human immmunoglobulin or hightitred rubella immunoglobulin. Although normal human immunoglobulin may reduce the incidence of clinically overt infection, subclinical infection may still occur. Since subclinical infection is accompanied by viraemia, there is still a risk of fetal infection. It has been shown that the infants of women who experienced subclinical rubella in early pregnancy following administration of normal immunoglobulin were less likely to be infected in utero, or, if infected, less severely affected, than infants of mothers not given this preparation. It is proposed that the immunoglobulin decreased viraemia and there was consequently less damage (reviewed by Hanshaw et al. Centers for Disease Control (2001a) Control and prevention of rubella: evaluation and management of suspected outbreaks, rubella in pregnant women, and surveillance for congenital rubella syndrome. In (eds Hansmann M, Feige A and Saling E) Pra Ёnatal-und Geberutsmedizin, Berichte vom 5th Kongress der Gesellschaft fur PranatalЁ Ё und Geburtsmedizin, 2123 February 1997. National Congenital Rubella Surveillance Programme (2003) Available from. Panagiotopoulos T, Antoniadou I and Valassi-Adam E (1999) Increase in congenital rubella occurrence after immunisation in Greece: retrospective survey and systematic review. Hudson P and Morgan-Capner P (1996) Evaluation of 15 commercial enzyme immunoassays for the detection of rubella-specific IgM. Institute of Medicine (2001) Immunization Safety Review: MeaslesMumpsRubella Vaccine and Autism.
Contemporary research evidence indicates that the majority of transmission events occur perinatally and during breast-feeding pain management for dog in heat purchase genuine imdur online. Studies of combination therapies are now under way to optimise regimens in relation to drug toxicity and duration of treatment eastern ct pain treatment center buy 20mg imdur visa. Trials of a single dose of nevirapine given to women in labour to prevent transmission have shown very good results pain treatment in acute pancreatitis cheap imdur 40 mg with mastercard. However fremont pain treatment center cheap imdur, one concern raised by these studies is the emergence of nevirapine resistance in some of these women-the rapidity of this process is probably associated with the slow decline in plasma levels following this one dose, creating an ideal selective pressure for resistance. Caesarean section gave early inconclusive results, but a recent meta-analysis of European and American studies showed a 55% reduction in risk of vertical transmission. Thus, at present the World Health Organization advises exclusive breast-feeding in Africa and avoidance in developed countries. Factors like time of infection, exposure to other pathogens, nutritional status, time of diagnosis and quality of care are all-important. Evidence suggests two groups of vertically infected infants: 30% with early clinical problems and life-threatening illnesses in the first year of life; and 70% with few problems in early life but who develop disease after several years. It has been proposed that these two groups represent early transplacental infection in the former and late infection in the latter. While this is plausible, one must also consider issues such as the pathogenicity of infecting viruses and immunological maturation, which may vary widely from case to case. Herpes simplex, varicella zoster and measles viruses all produce severe forms of the recognised presentations that require prompt and prolonged therapy to avoid high morbidity and mortality. Common paediatric bacterial infections, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. Prompt treatment is required until culture results are available, and multiple infections should always be suspected in unresolving cases. As in adults, opportunistic infections with Pneumocystis carinii, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. The reasons are multiple: sick mothers; decreased food intake due to oral infections; decreased absorption due to intestinal disease and recurrent diarrhoea; and decreased calorie utilisation for growth, due to demands associated with inflammatory responses and tissue repair. The use of antiretroviral therapies has improved the prognosis for all these clinical conditions. The algorithm for diagnosis of established adult disease is summarised in Figure 25. A positive report is released if consensus results are obtained from all three assays (490% of cases), and a second blood specimen is requested to confirm patient identity. This is repeated at weekly intervals and evolving signals in the serological assays confirm seroconversion. Patients with non-specific reactivity (presumed to have cross-reacting antibodies that signal in certain or all assays) show a distinctive virological pattern but present a difficult clinical problem. They often present through the blood transfusion service as a reactive sample on whom the donation has been withheld. They are followed over time for reassurance, support if they proceed to any other medical investigations, repeat testing at 6-monthly intervals, and in the majority the reactivity will eventually wane. Early diagnosis is essential for early clinical interventions and considerable effort has been applied to establishing algorithms. It takes up to 18 months for all passive antibody to disappear in the majority of infants and the analysis and reporting of these events involves considerable virological experience. These methods were useful to monitor the efficacy of antiretroviral therapy in trials (Katlama et al. These genome assays initially detected down to a level between hundreds and thousands of copies per ml plasma, but later second-generation assays defined cutoff values of around 2050 (Loveday, 1999). These viral load assays were initially used experimentally to define virological efficacy in clinical trials (Brun-Vezinet et al. A large cohort study revealed the predictive value of such measures for clinical outcome (Mellors et al. Thus, viral load was established as an essential marker, substituting for clinical endpoints, to define the efficacy of new antiretroviral drug combinations. In clinical practice, patients have regular viral load measures to assist the determination of disease stage, monitor progression, assess responses to antiretroviral therapies, and provide evidence of early treatment failure. Early in vitro studies and investigations of patients receiving monotherapies revealed that, as viral load response failed, drug-resistant viruses evolved in the plasma. These approaches were rapidly adapted for commercial assays, which allowed a wide availabilty of resistance testing in clinical virology laboratories to support patient care.
These researchers found that genetics account for about a third of the variation in bodily symptoms that are not clearly related to a medical disorder midsouth pain treatment center cordova order 20 mg imdur mastercard. Because of their particular cognitive biases regarding health and illness pain medication for dogs human order imdur 20mg on line, for people with hypochondriasis joint pain treatment in urdu buy imdur online pills, simply reading about an illness or hearing about someone who is sick can lead to becoming preoccupied with similar symptoms or diseases in their own bodies pain solutions treatment center atlanta buy 40mg imdur with amex. Psychological Factors: Catastrophic Thinking About the Body People with hypochondriasis have specific biases in their reasoning: Not surprisingly, given their disorder, they not only tend to seek evidence of health threats but also may fail to consider evidence that such threats are minimal or nonexistent (Salkovskis, 1996; Smeets, de Jong, & Mayer, 2000). For instance, a man with hypochondriasis who notices a bruise on his leg might interpret it as an indicator of leukemia rather than trying to remember whether he had recently bumped into something that could cause a black-and-blue mark. In addition, people afflicted with hypochondriasis focus attention closely on unpleasant sensations, even if those sensations are relatively weak or infrequent. They commonly focus on the functioning of body parts (such as the stomach or the heart), minor physical problems (such as a sore throat), and ambiguous physical sensations (such as "aching veins"). Moreover, they interpret bodily sensations as abnormal, pathological, and symptomatic of disease (Barsky, 1992; Barsky et al. As is the case with many anxiety disorders, people with hypochondriasis may engage in behaviors that temporarily reduce their anxiety. For example, they may repeatedly take their blood pressure, perform urine dipstick tests, feel body parts for cancerous lumps, or call their doctor about new symptoms. Such behaviors maintain their faulty beliefs and can, through negative reinforcement, sustain the anxiety in the long term. Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders 3 6 9 David Young-Wolff/PhotoEdit Inc People with hypochondriasis fear that they have a serious illness and do not believe their doctors when told that they are healthy. Such patients may then "doctor-shop"-consulting many doctors in search of one who will confirm the presence of an illness. Social Factors: Stress Response As with other somatoform disorders, stressful events can precipitate hypochondriasis (Fallon & Feinstein, 2001). Body Dysmorphic Disorder Body dysmorphic disorder (sometimes called dysmorphophobia) is diagnosed when someone is excessively preoccupied with a perceived defect or defects in appearance. The preoccupation is not better accounted for by another appears like a red beacon for others to see; many people will try to mental disorder. Common preoccupations for people with body dysmorphic disorder are thinning or excessive hair, acne, wrinkles, scars, complexion (too pale, too dark, too red, and so on), facial asymmetry, or the shape or size of some part of the face or body. The "defect" (or "defects") may change over the course of the illness (Phillips, 2001). People with body dysmorphic disorder may think that others are staring at Body dysmorphic disorder them or talking about a "defect. Alternatively, people with body dysmorphic disorder may try to avoid mirrors altogether. The preoccupation with-or attempts to hide-a perceived defect can be difficult to control and therefore devastating, consuming up to 8 hours each day (Phillips, 2001). Unfortunately, these behaviors, which are intended to decrease anxiety about appearance, end up increasing anxiety. A was an attractive 27-year-old single white female who presented with a chief complaint of "I look deformed. A was obsessed with many aspects of her appearance, including her "crooked" ears, "ugly" eyes, "broken out" skin, "huge" nose, and "bushy" facial hair. She estimated that she thought about her appearance for 16 hours a day and checked mirrors for 5 hours a day. She compulsively compared herself with other people, repeatedly sought reassurance about her appearance from her boyfriend and young son, applied and reapplied makeup for hours a day, excessively washed her face, covered her face with her hand, and tweezed and cut her facial hair. As a result of her appearance concerns, she had dropped out of high school and then college. Individuals who have body dysmorphic disorder may feel so self-conscious about a perceived defect that they avoid social situations (American Psychiatric Association, 2000), which results in their having few (or no) friends nor a romantic partner. Some try to get medical or surgical treatment for a "defect," such as plastic surgery, dental work, or dermatological treatment.
Order 40mg imdur amex. Guitarist With Arthritis and Bone Spurs In The Hand (Part 1).