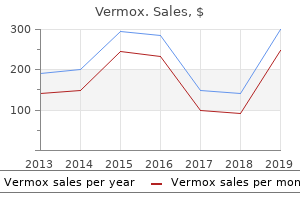
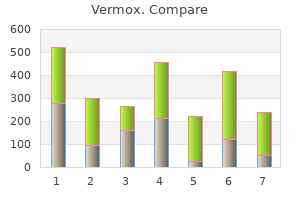
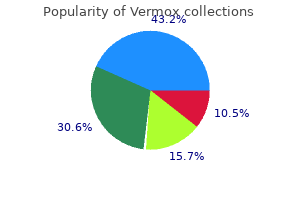
"Buy 100mg vermox, antivirus windows 8.1".
By: N. Norris, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine
When the walls of the rectum are stretched by the feces hiv timeline of infection discount 100mg vermox with visa, the defecation reflex is initiated and a bowel movement follows when this is convenient hiv infection undetectable viral load cheap vermox 100mg without a prescription. Haustrations are bulges in the large intestine caused by contraction of adjacent circular and longitudinal smooth muscle hcv hiv co infection rates discount 100mg vermox with amex. It should be clear that mass movements in the colon do not affect esophageal contractions or pharyngeal peristalsis hiv infection by kissing cheap vermox 100mg free shipping. This disorder slows or at times even stops the movement of chyme from the stomach to the duodenum. Diabetes is the most common known cause of gastroparesis; it occurs in about 20 percent of persons with type 1 diabetes. The high blood glucose is thought to damage the vagus nerve and thereby delay gastric emptying. C) Acid acts directly on somatostatin cells to stimulate the release of somatostatin. The somatostatin decreases acid secretion by directly inhibiting the acid-secreting parietal cells and indirectly by inhibiting gastrin secretion from G cells in the antrum. Fatty acids are a weak stimulus for motilin, but motilin does not affect gastrin release. C) All five gastrointestinal hormones are released from both the duodenum and jejunum. D) Primary peristalsis of the esophagus is a continuation of pharyngeal peristalsis; central control originates in the swallowing center located in the medulla and pons. Visceral somatic fibers in the vagus nerves directly innervate smooth muscle fibers of the pharynx and upper esophagus, which coordinate pharyngeal peristalsis and primary peristalsis of the esophagus. Esophageal contractions can occur independently of vagal stimulation by a local stretch reflex initiated by the food bolus itself; this phenomenon is called secondary peristalsis. Although the vagus nerves can stimulate gastric acid secretion, gastrin release, and pancreatic bicarbonate secretion, these processes can be activated by other mechanisms. D) Persons with duodenal ulcers have about 2 billion parietal cells and can secrete about 40 mEq H+ per hour. Plasma gastrin levels are related inversely to acid secretory capacity because of a feedback mechanism by which antral acidification inhibits gastrin release. Maximal acid secretion and plasma gastrin levels are not diagnostic for duodenal ulcer disease because of significant overlap with the normal population among persons in each group. C) Gastrin, acetylcholine, and histamine can directly stimulate parietal cells to secrete acid. These three secretagogues also have a multiplicative effect on acid secretion such that inhibition of one secretagogue reduces the effectiveness of the remaining two secretagogues. Acetylcholine also has an indirect effect to increase acid secretion by stimulating gastrin secretion from G cells. The patient has a diminished capacity to secrete acid because of chronic gastritis. Because acid and intrinsic factor are both secreted by parietal cells, a diminished capacity to secrete acid is usually associated with diminished capacity to secrete intrinsic factor. Ptyalin, also known as salivary amylase, is an enzyme that begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth. Rennin, known also as chymosin, is a proteolytic enzyme synthesized by chief cells in the stomach. Its role in digestion is to curdle or coagulate milk in the stomach, a process of considerable importance in very young animals. The parietal cell has receptors for secretagogues such as gastrin, acetylcholine, and histamine. Therefore, antigastrin antibodies, atropine, and histamine H2 blockers can reduce the secretion of acid, but none of these can completely eliminate acid secretion. Antacids neutralize gastric acid once it has entered the stomach, but they cannot inhibit acid secretion from parietal cells. C) this woman has celiac disease, also called glutensensitive enteropathy, which is a chronic disease of the digestive tract that interferes with the absorption of nutrients from food. Mucosal lesions seen on upper gastrointestinal biopsy specimens are the result of an abnormal, genetically determined, cell-mediated immune response to gliadin, a constituent of the gluten found in wheat; a similar response occurs to comparable proteins found in rye and barley. When persons with celiac disease ingest gluten, the mucosa of their small intestine is damaged by an immunologically mediated inflammatory response, which results in malabsorption and maldigestion at the brush border. Digestion of fat is normal in persons with celiac disease because lipase secreted by the pancreas still functions normally.
Choice A B C D E F Platelet count normal normal normal normal Bleeding time normal normal normal normal normal normal Prothrombin time normal normal normal Partial thromboplastin time 34 hiv infection dental work quality vermox 100 mg. A 3-year-old boy comes to the physician because of fever and erythema in his conjunctivae hiv infection no fever cheap vermox 100mg without prescription, oral mucosa antiviral kleenex bad vermox 100mg with mastercard, palms antiviral spices buy vermox 100mg cheap, and soles for the past week. Physical examination is significant for fever, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, and edema of the hands and feet. A 6-year-old boy arrives at the emergency department breathing rapidly and complaining of tinnitus and nausea. A 45-year-old man visited his primary care physician one month ago because of chest pain that he had experienced four times in the past four months. He has experienced this pain while watching television but has never felt it during exercise. R P T does this disease affect the pressures governing the flow of fluid across the glomeruli She is accompanied by her 45-year-old daughter, who is present because of their close relationship. During the visit, her daughter hears about the need for transplantation for the first time, and is visibly surprised, but declares that they will do "anything it takes. For which of the following reasons should consent be obtained from the daughter at a different time A 7-year-old boy presents to the physician with acute-onset edema and facial swelling. Renal biopsy shows no appreciable changes under light and fluorescence microscopy, but electron microscopy demonstrates glomerular epithelial cell foot process effacement. Physical examination is significant for 3+ edema in his lower extremities and 1+ edema in his hands and around his eyes. In addition to the underlying cause of his renal disease, which of the following comorbidities is most likely present in this patient A 35-year-old man presents to the physician with a two-month history of non-bloody, nonmucoid, non-oily watery diarrhea. He has a diastolic murmur that gets louder with inspiration and is best heard over the left lower sternal border. His face is warm and appears to be engorged with blood for several minutes during the examination. A screening test for disease X just came out, with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 70%. While being fitted for new glasses, the patient was found to have persistent constriction of his right pupil. After a thorough history and physical examination, x-ray of the chest was ordered, and results are shown in the image. Measurement and management of which of the following electrolytes are most critical in this patient His wife states that he has a history of benign prostatic hypertrophy and high blood pressure. According to the wife, the patient has never experienced symptoms like this before and has never had surgery of any type. Physical examination reveals an enlarged, tender, erythematous left axillary lymph node. Close inspection of the skin reveals a series of small linear scratches on the left forearm, with a nearby erythematous papule. Current Diagnosis & Treatment in Pulmonary Medicine, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003;. A 38-year-old white woman presents to the physician with a two-week history of aching pain in her left calf that is made worse by dorsiflexion of her foot. On physical examination, her left calf is found to be erythematous, warm, and swollen. Which of the following measures should she take to decrease similar problems in the future A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after his parents noted that he was acting confused and lethargic following several bouts of nausea and vomiting. A 35-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a chief complaint of palpitations and occasional chest pain.
It is possible that this patient has a hemothorax hiv infection rate romania buy vermox 100 mg fast delivery, but this vignette describes a pneumothorax injury hiv infection causes immunodeficiency because it purchase vermox 100mg with mastercard. The stab wound is above the nipple hiv infection nail salon discount vermox 100mg on-line, which is about the level of the fourth and fifth ribs anti viral ear drops buy vermox 100mg fast delivery, superior to the ninth and tenth ribs. It is possible that the man has also sustained injury to his lower ribs, but this would not be related to the knife injury and is not described in this vignette. Of note is the risk that a fractured lower rib (11th or 12th) may puncture the kidney, leading to retroperitoneal bleeding. A pleural effusion is seen on radiographs as a fluid collection in the dependent portions of the thorax. Pleural effusions can occur in heart failure, pneumonia, or iatrogenic fluid overload (eg, improper fluid management of a hospitalized patient). Right upper lobe consolidation would be consistent with right upper lobe pneumonia, which is not described in this vignette. One would expect to see a history of fever and other signs of infection, which is not the case here. Risedronate is a bisphosphonate used in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Although the exact mechanism of action of sulfasalazine is not known, it is believed to suppress the activity of natural killer cells and impair lymphocyte transformation, which would not directly allow mycobacteria to overcome immune surveillance and reactivate. Bronchiectasis can be caused by a chronic necrotizing infection of the bronchi leading to dilated airways. In addition to bronchopulmonary infections, bronchiectasis can be caused by bronchial obstructions or congenital abnormalities (bronchial cysts, tracheobronchial fistulas). Bronchiectasis is a common cause of hemoptysis and also frequently presents with cough and dyspnea. Adult respiratory distress syndrome causes diffuse alveolar damage that leads to increased alveolar capillary permeability. Short-acting b-agonists such as albuterol are used in the treatment of acute asthma exacerbations because of their relaxing effects on bronchial smooth muscle. Long-acting b-agonists such as salmeterol are used for prophylaxis of bronchospasm. Cromolyn inhibits antigen-induced bronchospasm by inhibiting mediator release from bronchial mast cells, and suppressing chemotaxis of neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes. Cromolyn is generally well tolerated, and adverse effects are generally minor, including bronchospasm, cough, wheezing, angioedema, headache, and nausea. Theophylline has a narrow therapeutic window and may cause cardiotoxicity (and neurotoxicity) but does not result in hypokalemia. Initial treatment of sarcoidosis includes a short course of glucocorticoids such as dexamethasone if the patient is symptomatic. For chronic disease, glucocorticoids may be continued or alternative agents such as methotrexate may be used. Small cell lung cancer is recognized by numerous small blue neoplastic cells on histologic exam. The image shows noncaseating granulomas, which are characteristic of sarcoidosis and would not be treated with chemotherapy. Goodpasture syndrome is caused by anti-basement membrane antibodies, which can be demonstrated on immunofluorescence. Initial treatment of Goodpasture syndrome is a five-day course of methylprednisolone followed by a long taper and maintenance. However, if the disease is particularly severe, immunosuppressive agents such as cyclophosphamide or azathioprine may be started. As this patient has sarcoidosis, not lupus, hydroxychloroquine would not be an appropriate treatment for her. Bacteria within the granuloma may not be destroyed, but may rather be dormant only to be later reactivated. If a patient is not rapidly treated with penicillin, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, or levofloxacin, systemic infection can cause septic shock (due to exotoxins produced by the bacteria) and death within 24 hours. Spores from sheep or goat skin are the primary mode of transmission in this kind of anthrax. Interestingly, B anthracis is the only medically relevant bacteria with a protein capsule. Brucella is transmitted from cattle to humans who have contact with infected animal meat, milk products, or aborted animal placentas.
On histopathology hiv virus infection process video buy vermox 100mg free shipping, the lesion consists of highly malignant astrocyte tumor cells that surround areas of necrosis; this is known as pseudopalisading hiv infection rates in african countries vermox 100mg low price. Densely packed cells with halos of cytoplasm surrounding large round nuclei are characteristic of oligodendrogliomas hiv infection rates in the world discount vermox 100 mg on-line, which are slow-growing tumors originating in the cerebral hemispheres how long from hiv infection to symptoms discount vermox master card. These lesions have a better prognosis than astrocytomas, with a mean patient survival of 5-10 years. The description is consistent with internuclear ophthalmoplegia, which consists of ipsilateral medial rectus palsy on attempted lateral conjugate gaze away from the lesion with associated monocular horizontal nystagmus in the contralateral abducting eye with preserved convergence. The third nerve and medial rectus muscle function normally in convergence but not during actions that require conjugate eye movements. In young patients, it is most commonly the result of central nervous system infection or multiple sclerosis, whereas in older patients it is more commonly the result of vascular disease. A pure sixth-nerve palsy would have almost the opposite effect of this scenario and would cause a lateral rectus palsy as opposed to a medial rectus palsy seen here. Pupillary light-near dissociation is also known as Argyll Robertson pupil and is an absent miotic reaction to light with preserved accommodation. This condition can occur in neurosyphilis, diabetes, and systemic lupus erythematosus. It results from a lesion in the afferent limb of the pupillary light reflex and can be seen in the retrobulbar neuritis of multiple sclerosis. The bone marrow aspirate is hypocellular without any abnormal cells, suggestive of aplastic anemia. Other causes of aplastic anemia include viruses (Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis C, and parvovirus B19), toxins (benzene and insecticides), and other drugs (cancer chemotherapeutics). Alcoholism has many metabolic and clinical sequelae, including decreases in all cell lines due to marrow suppression. However, the hypoplastic bone marrow and known antiepileptic drug use make the diagnosis of aplastic anemia most likely. This patient does have symptoms of thrombocytopenia, but the bone marrow aspirate should appear normal in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Pernicious anemia, the leading cause of megaloblastic anemia, does uncommonly occur in this age group. However, the bone marrow aspirate is not consistent with pernicious anemia, as this disease does not affect neutrophils, platelets, or any myeloid cell line other than erythrocytes. Although vitamin C deficiency can cause gingival bleeding, it does not cause anemia or a hypoplastic bone marrow. This risk is compounded greatly by smoking, making smoking an even riskier habit in someone with asbestosis. Silicotic nodules are seen in the lungs of patients with silicosis, while ferruginous bodies and ivory-white pleural plaques are seen in lungs of patients with asbestosis. Anthracosis (carbon deposits) is seen in patients exposed to pollution (usually seen in city-dwellers). This would grossly look like black spots on the lung, and is not considered to be pathologic. The patient has an increased risk of both mesothelioma and bronchogenic carcinoma. Silicosis, a disease caused by exposure to free silica dust, is associated with increased tuberculosis susceptibility. Lungs with asbestosis have diffuse pulmonary interstitial fibrosis caused by inhaled asbestos fibers. Sickle cell anemia also is characterized by splenic sequestration (with eventual functional asplenia and an increased risk for sepsis and osteomyelitis), cerebrovascular accidents, and acute chest syndrome. Acute chest syndrome is a severe complication of vasoocclusive disease and presents with chest pain, hypoxemia, and chest infiltrates. Because hypoxemia can instigate further sickling and pulmonary vasoocclusion, acute chest syndrome is an indication for emergent exchange transfusion. In this disorder, dysplastic megakaryocytes produce increased fibroblast growth factors, leading to marrow fibrosis and marrow failure. Eosinophilia is associated with parasite infection and would not explain the sickled cells seen in the image.
Order 100 mg vermox with visa. 15 new HIV cases reported in Larkana | 25 April 2019 | 92NewsHD.