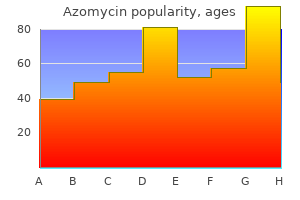
"Order generic azomycin from india, antibiotic resistance from animals to humans".
By: Q. Felipe, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Western University of Health Sciences
This causes a sharp rise in intraocular pressure for a short period of time followed by a spontaneous resolution of the pupillary block possibly due to: i infection 1d azomycin 250mg online. Sleep (As the pupil becomes constricted) Emotional stress may also be a precipitating factor antibiotic qualities of honey order azomycin 500 mg. Coloured halos around lights-There is accumulation of fluid in the corneal epithelium and corneal lamellae which alters the refractive conditions of the cornea get smart antibiotic resistance questions and answers purchase generic azomycin from india. As halos are seen as coloured rings around lighted bulb antibiotics for sinus infections in adults generic azomycin 250mg on-line, they are observed only after dark. The colours are distributed as in the spectrum of rainbow with red colour being outside and violet inner most. Course Some eyes may develop an acute attack or may progress into chronic primary angle-closure glaucoma. Diagnosis Diagnosis in the early stages (angle-closure suspect and intermittent or subacute angle-closure) is important since adequate treatment at this stage is easy and certain to prevent the loss of vision. If the patient gives a vague history, the halo can be demonstrated by him on looking through a thin layer of lycopodiun powder enclosed between two glass plates made up as a trial lens. Provocative tests- Rise in tension can be tested by the provocative tests even if the tension is normal. Dark room test-The patient lies awake in the prone (with face downward) position in a dark room for 1 hour. The pupil dilates and if the rise in tension is more than 8 mm Hg (Schiotz), it is pathological. Full miosis is achieved after the test by the instillation of pilocarpine eyedrops as precaution. Lenticular halos-These are typically seen in early cataractous changes in the lens. Lenticular halo-It is broken up into segments which revolve as the slit is moved. It is typically seen in the case of incipient cataract due to the prismatic effect of the wedge-shaped peripheral cortical opacities where the halos "make and brake". Halo in conjunctivitis-This is due to the sticking of conjunctival discharge on the cornea. The stenopaeic test (Fincham test) Treatment Prophylactic peripheral laser iridotomy is performed in both eyes of all the patients because if untreated the risk of acute pressure rise during the next 5 years is very high (50% approximately). Glaucoma 285 Mechanism of the rise in intraocular pressure in angle-closure glaucoma Pathogenesis the crisis is due to acute ischaemia associated with liberation of prostaglandin-like substances. If the attack lasts for several hours or days, irreversible damage may occur to the ocular tissues. Severe unilateral headache, nausea, vomiting and prostration are often associated. There is sudden onset of intense unbearable pain in the eye due to stretching of the sensory nerves. It is mainly due to ischaemia due to optic neuropathy and partially due to corneal oedema stasis and increased permeability of the capillaries. Redness, lacrimation and photophobia are present due to corneal oedema erosion and conjunctival and ciliary congestion. Lens-Glaucoma fleckens are small greyish white anterior subcapsuler opacities seen in the lens in the pupillary area. Fundus examination-There may be difficulty in visualizing the fundus due to hazy cornea. Gonioscopy-It reveals abnormally narrow angle of the anterior chamber with or without anterior synechiae. Peripheral anterior synechiae (organized exudates) occur as a result of prolonged and repeated acute congestive attack. The perfusion of optic nerve head is affected due to decreased blood flow in the capillary and in annulus of Zinn which supplies nutrition to the laminar and post-laminar optic nerve head. It usually passes into the stage of chronic primary angle-closure glaucoma as the angle becomes slowly and progressively closed. Treatment Although the treatment of primary angle-closure glaucoma is essentially surgical, the initial treatment is medical in order to control the raised tension. Medical Treatment It is useful in lowering the raised tension particularly in the acute congestive attack preoperatively.
Severity of hypertension-It is reflected by the vascular changes and retinopathy horse antibiotics for dogs buy 100 mg azomycin with visa. Duration of hypertension-It is indicated by the degree of arteriosclerotic changes and retinopathy infection 5 metal militia purchase generic azomycin from india. Pathogenesis Essential hypertension with sustained elevation of blood pressure results in i infection 3 weeks after abortion buy azomycin with a mastercard. Vasoconstriction-Narrowing of the retinal arterioles is related to the severity of hypertension antibiotic quick guide best buy azomycin. It occurs in pure form in young persons but it is affected by the pre-existing involutional sclerosis in the older patients. Arteriolosclerosis changes-These manifest as changes in arteriolar reflex and A-V crossing changes. In aged patients, arteriolosclerotic changes are already present (involutional sclerosis). Increased vascular permeability-This results from retinal ischaemia (hypoxia) and is responsible for haemorrhages, exudates (soft and hard) and retinal oedema. Hypertensive Choroidopathy this typically occurs in young patient experiencing acute hypertension, such as patient with preeclampsia, eclampsia or accelerated hypertension. Elschnig spots are small, black spots surrounded by yellow halos which represent focal choroidal infarcts. Siegrist streaks are flecks which are arranged lineraly along the choroidal vessels. Keith Wagner and Barker (1939) Keith, Wagner and Barker (1939) have classified hypertensive retinopathy into four grades on the basis of ophthalmoscopic characteristics. It correlates directly with the degree of hypertension and inversely with the prognosis for survival of patients. Grade 1 Mild to moderate narrowing or sclerosis of the retinal arterioles is present. These patients have benign essential hypertension with adequate cardiorenal function. Copper wire reflex-When the transparent arterial wall becomes thick and reflects light, the reflex looks wider and burnish copper coloured. Silver wire reflex-Marked thickening of the arterial walls causes all the light to reflect and the artery looks brilliant white. Cotton wool or soft exudates consisting of fibrin and protein are scattered all over the fundus. Macular star is formed due to accumulation of hard exudates in the outer plexiform layer. Prognosis-These patients have grave prognosis and their life expectancy is one year if untreated. Grade 2 - Severe narrowing with localized irregular constriction of the arterioles. Grade 3 - Narrowing and focal irregularities of arterioles, retinal haemorrhage and exudates. Grade 4 - All changes in grade 3 along with neuroretinal oedema, and / or papilloedema. Arteriolo-sclerotic features these changes develop if the hypertension is present over a period of many years, and are mainly seen in aged individual. The Retina 315 Clinical Types Clinically, hypertensive retinopathy may occur in four forms as follows: 1. Energetic treatment with antihypertensive drugs results in remarkable improvement of the fundus picture.
Heart Murmurs Heart murmurs are relatively prolonged series of auditory vibrations of variable intensity antibiotics for uti feline purchase cheap azomycin on line, quality and frequency antibiotic resistance mayo clinic buy azomycin online now. It is due to turbulence that arises when blood velocity increases due to increased flow or due to flow through a constricted or irregular orifice antibiotic and yeast infection purchase azomycin 100mg with visa. In nonvalvular aortic or pulmonary stenosis antimicrobial x ray jackets cheap azomycin 100mg with visa, the intensity of A2 or P 2 is normal respectively. Conduction Accentuation with respiration To axilla, base and back In expiration In inspiration. It is generated by flow of blood from a zone of high resistance to a zone of low resistance without interruption during both systole and diastole. Acute severe aortic regurgitation (it is due to the diastolic flutter of the anterior mitral leaflet by the regurgitant blood stream). Systemic to pulmonary communication Patent ductus arteriosus Aortopulmonary window Tricuspid atresia Pulmonary atresia Anomalous origin of left coronary artery from pulmonary artery. Systemic to right heart connection Coronary arteriovenous fistula Rupture of sinus of Valsalva. Normal flow through constricted arteries Coarctation of aorta Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis Carotid stenosis Coeliac artery stenosis Mesenteric artery stenosis Renal artery stenosis. Venous (Diastolic accentuation) Cervical venous hum Umbilical vein (Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur). Arterial (Systolic accentuation) Mammary souffle Uterine souffle Hepatoma Nephroma Thyrotoxicosis. Approach to Continuous Murmurs An approach to the differential diagnosis, when a continuous murmur is heard, is done by assessing the following: 1. To and Fro Murmurs (Biphasic Murmurs) A murmur occurring through a single channel and occupying midsystole and early diastole and does not peak around S2. S2 engulfed by the murmur To and fro murmur Bidirectional S2 heard well Cardiovascular System 105 Systolico-diastolic Murmur A murmur that occupies systole and diastole and occurs through different channels and does not peak around S2. Diastolic Murmurs Mid diastolic flow murmurs: Mid-diastolic flow murmurs may be heard over the mitral or tricuspid areas, the causes of which have already been discussed. They are short, soft (grade 3/6 or less), systolic murmurs usually heard over supraclavicular area and along the sternal borders. Changing Murmurs these are murmurs which change in character or intensity from moment to moment. Dynamic Auscultation Dynamic auscultation refers to the changes in circulatory haemodynamics by physiological and pharmacological manoeuvres and about the effect of these manoeuvres on the heart sounds and murmurs. Respiration Murmurs that arise on the right side of the heart becomes louder during inspiration as this increases venous return and therefore blood flow to the right side of the heart. Expiration has the opposite effect (Left sided murmurs are louder during expiration). Deep Expiration the patient leans forward during expiration to bring the base of the heart close to the chest wall and in this posture aortic regurgitant murmur and the scraping sound of a pericardial friction rub are better heard. Valsalva Manoeuvre In this manoeuvre, patient is advised to close the nose with the fingers and breathe out forcibly with mouth closed against closed glottis. Functional Murmurs these are murmurs caused by dilatation of heart chambers or vessels or increased flow. Phase 2: During straining phase, systemic venous return falls resulting in reduced filling of right and left ventricle. Phase 3: During the release phase, first the right sided and then the left sided cardiac murmurs become louder briefly before returning to normal. Standing to Squatting When the patient suddenly squats from the standing position, venous return and systemic arterial resistance increase simultaneously causing a rise in stroke volume and arterial pressure. Squatting to Standing When the patient stands up quickly after squatting the opposite changes occur. Isometric Exercise Sustained hand grip for 20-30 seconds increases systemic arterial resistance, blood pressure and heart size. The systolic murmur of aortic stenosis may become softer because of the reduction in the pressure gradient across the valve, but often remains unchanged. The same vector records a small and equiphasic complex in the lead which is perpendicular to the previous one.
Purchase 500mg azomycin mastercard. Abdullah Farooq - Breaking the Wall of Antibiotic Resistance with Phage Therapy.
Pathogenesis Chronic dacryocystitis There are two main factors resulting in a vicious cycle: 1 bacteria h pylori espanol cheap 500 mg azomycin mastercard. Stasis of sac content-The anatomical factors responsible for stasis are narrow lumen of nasolacrimal duct antibiotics for uti and pneumonia discount 500 mg azomycin. Infection-It may ascend from nose bacteria 5 second rule cartoon purchase azomycin from india, descend from conjunctiva or spread from vicinity antibiotic brand names discount azomycin generic. There is constant epiphora or passive overflow of tears over the lid margin which is aggravated by exposure to wind. There is swelling, pain and redness at the site of the sac (mucocele) in cases of acute or recurrent infection. Persistent congestion of the neighbouring conjunctiva, caruncle and skin may be seen. Atonic sac-The contents of the atonic sac can be evacuated by external pressure only. Lacrimal abscess may occur following probing or spontaneously due to pyogenic infection. Radiological examination-The lacrimal passage is visualized radiographically by: i. X-ray is taken immediately and after 10-15 minutes to find out the size of the sac and site of obstruction. Subtraction macrodacryocystography with canalicular catheterization is a more accurate diagnostic technique. Radioactive tracer containing sulphur is instilled into the conjunctival sac and its excretion is visualized by gamma camera. In recent cases Repeating syringing of the nasolacrimal duct and frequent instillation of antibiotic drops is indicated in recent cases. Therapeutic-Syringing is curative in early cases by separating the oedematous mucosal walls sticking together and by clearing the mucosal debris. Principle-It reduces the swelling of the inflamed mucosa and restores the patency of lacrimal excretory passage by clearing the epithelial debris. Conjunctival sac is anaesthetized by frequent instillation of topical xylocaine or other suitable local anaesthetic. Lacrimal sac is syringed out 2-3 times using 24-26 gauge cannula attached to 5 cc syringe filled with normal saline and antibiotic drops are instilled. Dacryocystectomy-The lacrimal sac is excised completely in elderly persons specially if the lacrimal sac is fibrosed. Dacryocystorhinostomy-It is a nasal drainage operation performed in young and adult patients. The sac must be of normal size in order to anastomose it with the healthy nasal mucosa. The lacrimal sac and the area surrounding it is anaesthetized by an injection of local anaesthetic. A curved incision 2 mm above the medial palpebral ligament, 3 mm to the nasal side of inner canthus and 4 mm downwards and outwards is given. Orbicularis muscle is sutured with catgut and the skin is sutured with continuous subcuticular sutures preferably for cosmetic purpose. Normal position of lacrimal sac in lacrimal fossa 434 Basic Ophthalmology Complication Epiphora may persist for sometime and then it gradually wears off. It has the advantage over dacryocystectomy as there is no epiphora or watering of eyes postoperatively. The nasal mucosa of the middle meatus is anastomosed with the medial wall of the sac by making vertical incisions in them.