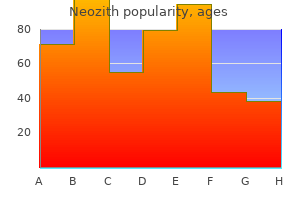
"500mg neozith for sale, infection 2 bio war simulation".
By: Z. Rhobar, M.A.S., M.D.
Professor, University of Toledo College of Medicine
When biomedical engineers work within a hospital or clinic infection 10 days after surgery cheap neozith online mastercard, they are more properly called clinical engineers bacterial chromosome discount neozith 100mg with mastercard. Activities of Biomedical Engineers the breadth of activity of biomedical engineers is now significant antibiotics ending with mycin buy generic neozith online. The field has moved from being concerned primarily with the development of medical instruments in the 1950s and 1960s to include a more wide-ranging set of activities antimicrobial gym bag for men cheap neozith 500mg with mastercard. As illustrated below, the field of biomedical engineering now includes many new career areas (see Figure 1), each of which is presented in this handbook. Accordingly, like medical practice itself, it is unlikely that any single person can acquire expertise that encompasses the entire field. Yet, because of the interdisciplinary nature of this activity, there is considerable interplay and overlapping of interest and effort between them. For example, biomedical engineers engaged in the development of biosensors may interact with those interested in prosthetic devices to develop a means to detect and use the same bioelectric signal to power a prosthetic device. Those engaged in automating the clinical chemistry laboratory may collaborate with those developing expert systems to assist clinicians in making decisions based on specific laboratory data. Perhaps a greater potential benefit occurring from the use of biomedical engineering is identification of the problems and needs of our present healthcare system that can be solved using existing engineering technology and systems methodology. Consequently, the field of biomedical engineering offers hope in the continuing battle to provide high-quality care at a reasonable cost. If properly directed toward solving problems related to preventive medical approaches, ambulatory care services, and the like, biomedical engineers can provide the tools and techniques to make our healthcare system more effective and efficient; and in the process, improve the quality of life for all. He is the author of over 200 articles and 11 books including the following: Technology for Patient Care (C. Abbas Center for Rehabilitation Neuroscience and Rehabilitation Engineering the Biodesign Institute Arizona State University Tempe, Arizona Pamela J. Hoyes Beehler University of Texas-Arlington Arlington, Texas Fernando Casas Department of Biomedical Engineering the Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio Edward J. Berbari Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, Indiana Andrea Caumo San Raffaele Scientific Institute Milan, Italy Kai-Nan An Biomedical Laboratory Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota R. Chandran Department of Biomedical Engineering College of Engineering University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa W. Billotte University of Dayton Dayton, Ohio Isabel Arcos Alfred Mann Foundation for Scientific Research Sylmar, California Joseph D. Bardakjian Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario, Canada K. Burg Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, North Carolina Claudio Cobelli Department of Information Engineering University of Padova Padova, Italy Thomas J. Burkholder School of Applied Physiology Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia Roger C. Barr Department of Biomedical Engineering School of Engineering Duke University Durham, North Carolina Rory A. Cooper School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Thomas R. Ross Davis Neural Engineering Clinic Melbourne Beach, Florida Alfred Mann Foundation for Scientific Research Sylmar, California Michael J. Furey Mechanical Engineering Department Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg, Virginia Robert M. Hochmuth Department of Mechanical Engineering Duke University Durham, North Carolina Roy B. Hurley Department of Kinesiology College of Health and Human Performance University of Maryland College Park, Maryland Peter A.
The occurrence of a periodic pattern of motor activity virus in the heart order neozith pills in toronto, comprising bursts of contractions alternating with "intervals of repose bacteria reproduce asexually by buy line neozith," in the gastrointestinal tracts of fasted animals was noted early in the 20th century by Boldireff [1905] virus 2014 respiratory virus buy 500 mg neozith mastercard. Periodic bursts of activity were also observed in (1) the lower esophageal sphincter antibiotics raise blood sugar order discount neozith on line, [Cannon and Washburn, 1912], and (2) the pylorus [Wheelon and Thomas, 1921]. Further investigation of the fasting contractile activity in the upper small intestine was undertaken in the early 1920s with particular emphasis on the coordination between the stomach and duodenum [Wheelon and Thomas, 1922; Alvarez and Mahoney, 1923]. With the use of implanted strain gauges, it was possible to observe contractile activity over long periods of time and it was demonstrated that the cyclical fasting pattern in the duodenum was altered by feeding [Jacoby et al. The types of contractions observed during fasting and feeding were divided into four groups [Reinke et al. Three types of contractile patterns were observed in fasted animals (1) quiescent interval, (2) a shorter interval of increasing activity, and (3) an interval of maximal activity. The fourth type was in fed animals and it consisted of randomly occurring contractions of varying amplitudes. With the use of implanted electrodes in the small intestine of fasted dogs, Szurszewski [1969] demonstrated that the cyclical appearance of electrical spiking activity at each electrode site was due to the migration of the cyclical pattern of quiescence, increasing activity, and maximal electrical activity down the small intestine from the duodenum to the terminal ileum. Grivel and Ruckebusch [1972] demonstrated that the mechanical correlate of this electrical pattern, which they called the migrating motor complex, occurs in other species such as sheep and rabbits. They also observed that the velocity of propagation of the maximal contractile activity was proportional to the length of the small intestine. Bursts of distally propagating contractions have been noted in the gastrointestinal tract of man [Beck et al. Control cycle is one depolarization and repolarization of the transmembrane voltage. Control wave (or slow wave) is the continuing rhythmic electrical activity recorded at any one site. It was assumed to be generated by the smooth muscle cells behaving like a relaxation oscillator at that site. Response Potentials (or spikes) are the rapid oscillations of transmembrane voltage in the depolarized state of smooth muscle cells. They are associated with muscular contraction and their occurrence is assumed to be in response to a control cycle when acetylcholine is present. Initially, the electrical and mechanical patterns were referred to as the migrating myoelectric complex and the migrating motor complex, respectively. It has two curvatures, the greater curvature which is four to five times as long as the lesser curvature, and it consists of three namely, regions: the fundus, the corpus (or body), and the antrum, respectively. The outermost layer is the longitudinal muscle layer, the middle is the circular muscle layer, and the innermost is the oblique muscle layer. These layers thicken gradually in the distal stomach toward the pylorus, which is consistent with stomach function since trituration occurs in the distal antrum. In an adult male, its greatest length when distended is about 25 to 30 cm and its widest diameter is about 10 to 12 cm [Pick and Howden, 1977]. The structural relationships of nerve, muscle, and interstitial cells of Cajal in the canine corpus indicated a high density of gap junctions indicating very tight coupling between cells. There is a marked intrinsic frequency gradient along the axis of the stomach and a slight intrinsic frequency gradient along the circumference. Also, there is an orad to aborad intrinsic gradient in resting membrane potential, with the terminal antrum having the most negative resting membrane potential, about 30 mV more negative than the fundal regions [Szurszewski, 1987]. The relatively depolarized state of the fundal muscle may explain its electrical inactivity since the voltage-sensitive ionic channels may be kept in a state of inactivation. Hyperpolarization of the fundus to a transmembrane voltage of -60 mV produces fundal control waves similar to those recorded from mid and orad corpus. The model featured (1) an intrinsic frequency decline from corpus to the pylorus and from greater curvature to the lesser curvature, (2) entrainment of all coupled oscillators at a frequency close to the highest intrinsic frequency, and (3) distally decreasing phase lags between the entrained oscillators. A simulated circumferential transection caused the formation of another frequency plateau aboral to the transection. The frequency of the orad plateau remained unaffected while that of the aborad plateau was decreased. The duodenum extends from the pylorus to the ligament of Treitz (about 30 cm in humans and dogs). In humans, the duodenum forms a C-shaped pattern, with the ligament of Treitz near the corpus of the stomach.
Clinical features and prognosis of herpetic anterior uveitis: a retrospective study of 111 cases virus examples generic 500mg neozith fast delivery. Long term acyclovir use to prevent recurrent ocular herpes simplex virus infection antibiotic 294 order 250 mg neozith free shipping. Clinical features of cytomegalovirus anterior uveitis in immunocompetent patients infection bio war cheats cheap neozith 250 mg fast delivery. Presumed fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis and Posner-Schlossman syndrome: comparison of cytomegalovirus-positive and negative eyes virus game buy neozith 500 mg on-line. Fuchs heterochromic cyclitis: rubella virus antibodies and genome in aqueous humor. Immune-recovery uveitis in patients with cytomegalovirus retinitis taking highly active antiretroviral therapy. Diagnosis of tuberculous uveitis: clinical application of an interferon-gamma release assay. Sub-retinal fibrosis and choroidal neovascularization in Vogt Koyanagi-Harada syndrome. Revised diagnostic criteria for vogt-koyanagi-harada disease: considerations on the different disease categories. Sympathetic ophthalmia: incidence of ocular complications and vision loss in the sympathizing eye. A randomized, masked, cross-over trial of acetazolamide for cystoid macular edema in patients with uveitis. Guidelines for the use of immunosuppressive drugs in patients with ocular inflammatory disorders: recommendations of an expert panel. Recent advances in drug delivery systems for treating ocular complications of systemic diseases. Ocular Oncology this list is not exhaustive and the reading material is recommended and not required. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in uveal melanoma: a predictor for metastatic disease and a potential therapeutic target. The dynamics of serum tumor markers in predicting metastatic uveal melanoma (part 1). Ten year results of transscleral resection of large uveal melanomas:Local tumor control and metastatic rate. Transformation of cell type in uveal melanomas: a quantitative histologic analysis. Systemic therapy for unresectable metastatic melanoma: impact of biochemotherapy on long-term survival. Prognostic biomarkers in uveal melanoma: evidence for a stem cell-like phenotype associated with metastasis. Late radiation failures after iodine 125 brachytherapy for uveal melanoma compared with charged-particle (proton or helium ion) therapy. Estimates of ocular and visual retention following treatment of extra-large uveal melanomas by proton beam radiotherapy. Psychological aspects of cytogenetic testing of uveal melanoma: preliminary findings and directions for future research. Reconciling the principle of patient autonomy with the practice of informed consent: decision-making about prognostication in uveal melanoma. Routes of Extraocular Extension of Uveal Melanoma Risk Factors and Influence on Survival Probability. A reappraisal of the significance of largest basal diameter of posterior uveal melanoma. Genotypic profiling of 452 choroidal melanomas with multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Artificial Neural Networks Estimating Survival Probability after Treatment of Choroidal Melanoma. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment after transscleral local resection of choroidal melanoma.
Buy neozith discount. Antimicrobial Resistance workshop - Introduction.