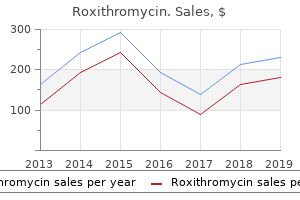
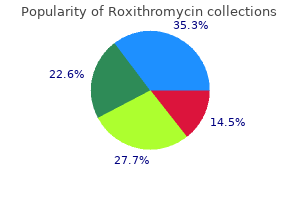
"Buy roxithromycin 150mg mastercard, bioban 425 antimicrobial".
By: S. Fasim, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Deputy Director, Florida Atlantic University Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine
Many acoustical and timing parameters can be adjusted to improve the audibility in a noisy environment as well as elicit a desired response from the listener antibiotics for uti breastfeeding buy generic roxithromycin. This set of experiments studied the effect of pulse parameters in these auditory warning signals on perceived urgency and response time in the presence of background noise urinalysis bacteria 0-5 buy roxithromycin with amex. The simultaneous pulse consisted of four pure tones at (500 virus b buy roxithromycin 150 mg with amex, 1000 antibiotic yellowing of teeth discount 150mg roxithromycin otc, 2 000 and 3 000) Hz, sounding simultaneously during a single pulse duration. The sequential pulse consisted of four pure tones at (500, 1 000, 2 000, and 3 000) Hz, sounding sequentially during a single pulse duration. The sawtooth frequencymodulated pulse format consisted of a pure tone carrier that rose and fell in a sawtooth pattern between 500 Hz and 3 000 Hz during a single pulse duration. The interpulse interval is defined as the time duration between the end of the offset of one pulse to the onset of the next. The environments of interest for this study were military or industrial settings that contain machinery generating steadystate noise, in which operators experience a high level of demand for their attention. The noise in these environments can be represented by pink noise, which contains equal amounts of energy in octave bands. They were given a standard workload task in order to impose demands on their attention. Participants were presented with auditory signals containing combinations of the three independent variables tested in this study (pulse format, pulse level, and interpulse interval), which resulted in 18 different auditory signals. After a 10 min break, their response time to each signal was measured by how long it took to press a button on a onebuttonkeypad with their dominant hand while performing the workload task. After a 30 min break, the participants were presented with 153 signal pair combinations (all unique combinations of 18 signals taken two at a time) in random order and asked to indicate which signal from each pair was more urgent. The workload task was assessed to be sufficiently demanding on the attention of the participants for the purposes of this experiment. The results showed that perceived urgency increased strongly with increasing pulse level. Signals with shorter interpulse intervals were perceived as significantly more urgent, with signals with no interpulse interval (zero ms) considered the most urgent. For each signal type, urgency was rated highest when the 81 this publication is available free of charge from: doi. Finally, sequential signals were rated as significantly less urgent than simultaneous and frequency modulated signals. Response time was significantly shorter for the highest pulse level than for the lowest, with a difference of 60 ms. Although this is a very short delay, it can make a difference in a job requiring immediate response, such as piloting a fighter jet. The mean response time for sequential signals was significantly greater (up to 40 ms) than for simultaneous and frequency modulated signals. The correlation between results for perceived urgency and response time indicates that response time is fastest when perceived urgency is greatest. Through variation of parameters, proper design of pulsebased signals can assist listeners in deciding how urgently they need to respond. Certain signal characteristics can be modified to match the urgency perceived by the listener with the urgency required by the situation. For operators engaged in a task in a noisy environment, response time was shorter by 60 ms for a higher pulse sound level compared to that for a lower pulse level. Discipline: Acoustics/Audiology Rating: 7B Auditory signals are often used to monitor high risk situations, such as patients at a hospital, or gauges in an airplane cockpit. However, it has been shown that the urgency of these signals do not always match the urgency of the situation at hand. This results in people either ignoring the signals, or turning them off due to their annoying and distracting nature.
Right ventricular infarction: frequency antibiotics in chicken 150mg roxithromycin with mastercard, size and topography in coronary heart disease: a prospective study comprising 107 consecutive autopsies from a coronary care unit treatment for sinus infection in child purchase roxithromycin online from canada. Phase and amplitude imaging in the diagnosis of acute right ventricular damage in inferior infarction antibiotic with least side effects purchase 150mg roxithromycin with visa. The evaluation of right ventricular function in acute myocardial infarction by xenon-133 antibiotic resistance agriculture purchase 150mg roxithromycin mastercard. Right ventricular infarction as an independent predictor of prognosis after acute inferior myocardial infarction. Isolated right ventricular infarction due to occlusion of the right ventricular branch in the absence of percutaneous coronary intervention. In-hospital outcome of elderly patients with acute inferior myocardial infarction and right ventricular involvement. Primary angioplasty versus intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: a quantitative review of 23 randomised trials. Right ventricular myocardial infarction with anterior wall left ventricular infarction: an autopsy study. Effects of thrombolytic therapy in acute inferior myocardial infarction with or without right ventricular involvement. Right ventricular infarction: role of the moderator band artery in determining infarct size. Comparison of effectiveness of primary angioplasty for proximal versus distal right coronary artery culprit lesion during acute myocardial infarction. Right ventricular function evaluated by radionuclide angiography in acute myocardial infarction. Volume loading improves low cardiac output in experimental right ventricular infarction. Importance of left ventricular function and systolic ventricular interaction to right ventricular performance during acute right heart ischemia. Hemodynamic importance of systolic ventricular interaction, augmented right atrial contractility and atrioventricular synchrony in acute right ventricular dysfunction. Physical examination for exclusion of hemodynamically important right ventricular infarction. Prognostic significance of complete atrioventricular block in patients with acute inferior myocardial infarction with and without right ventricular involvement. Bedside recognition, incidence and clinical course of right ventricular infarction. Interventional post-myocardial infarction ventricular septal defect closure: a systematic review of current evidence. Right ventricular infarction complicated by right to left shunting through an atrial septal defect: successful treatment with an Amplatzer septal occluder. Patterns of coronary compromise resulting in acute right ventricular ischemic dysfunction. Sensitivity and specificity of hemodynamic criteria in the diagnosis of acute right ventricular infarction. The pulmonary artery pulsatility index identifies severe right ventricular dysfunction in acute inferior myocardial infarction. Value of two-dimensional echocardiography, electrocardiography, and clinical signs in detecting right ventricular infarction. Serial evaluation of right ventricular dysfunction associated with acute inferior myocardial infarction. Effect of reperfusion on biventricular function and survival after right ventricular infarction. Right ventricular infarction: recognition and assessment of its hemodynamic significance by two-dimensional echocardiography. Inversion of the normal interatrial septum convexity in acute myocardial infarction: incidence, clinical relevance and prognostic significance.
Purchase roxithromycin 150mg visa. Review Equate Dry Mouth Oral Rinse.
Immunodiagnostic techniques diagnose disease by detection of agent-specific antigens and/or antibodies present in clinical samples quinolone antibiotic resistance cheap roxithromycin. The most significant problem associated with development of an integrated diagnostic system is the inability of immunodiagnostic technologies to detect agents with sensitivities approaching those of more sensitive nucleic acid-detection technologies antibiotic 500g 150 mg roxithromycin mastercard. These differences in assay sensitivity increase the probability of obtaining disparate results infection next to fingernail purchase roxithromycin australia, and they could therefore actually complicate medical decisions antibiotics for acne inflammation cheap roxithromycin 150 mg with amex. However, continued advances in immunodiagnostic technologies provide the basis for developing antigen- and antibody-detection platforms capable of meeting requirements for sensitivity, specificity, assay speed, robustness, and simplicity. Detection of specific proteins or other antigens or host-produced antibodies Laboratory Identification of Threats directed against such antigens constitutes one of the most widely used and successful methods for identifying biological agents and for diagnosing the diseases they cause. Nearly all methods for detecting antigens and antibodies rely on production of complexes made of one or more receptor molecules and the entity being detected (Figure 26-5). Diagnosing disease using immunodiagnostic technologies is a multistep process involving formation of complexes bound to a solid substrate. This process is like making a sandwich in which detecting the biological agent or antibody depends on incorporation of all of the sandwich components. The assays are relatively simple and robust, but elimination of any one part of the sandwich results in a failure and a negative response. Primary ligands used in most immunoassays are polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies or antibody fragments. Generally, the first step in an immunodiagnostic assay is binding one or more antibodies for the target of interest onto a solid support. Immunoassays are either heterogeneous or homogeneous depending on the nature of the solid substrate. A heterogeneous assay requires physical separation of bound from unbound reactants by using techniques such as washing or centrifugation. These types of assays can remove interfering substances and are, therefore, usually more specific. Heterogeneous assays require more steps and increased manipulation that cumulatively affect assay precision. A homogeneous assay requires no physical separation but may require pretreatment steps to remove interfering substances. Homogeneous assays are usually faster and more conducive to automation because of their simplicity. However, the cost of these assays is usually greater because of the types of reagents and equipment required. Once the test sample is reacted with the capture element, the final step in any immunoassay is detection of a signal generated by one or more assay components. This detection step is typically accomplished by using antibodies bound to (or labeled with) inorganic or organic molecules that produce a detectable signal under specific chemical or environmental conditions. However, radioisotope labels have generally been replaced with less cumbersome labels such as enzymes. Enzymes are effective labels because they catalyze chemical reactions, which can produce a signal. Depending on the nature of the signal, reactants may be detected visually, electronically, chemically, or physically. A single enzyme molecule can catalyze many chemical reactions without being consumed in the reaction; therefore, these labels are effective at amplifying assay signals. The target of interest (direct and indirect assays) or a capture antibody (sandwich assay) is immobilized by direct adsorption to a solid support such as a 96-well plate or magnetic bead. Detection of the target is accomplished using an enzyme-conjugated primary antibody (direct assay) or a matched set of unlabeled primary and conjugated secondary antibodies (indirect and sandwich assays). Fluorescent dyes and other organic and inorganic molecules capable of generating luminescent signals are also commonly used labels in immunoassays. Assays using these molecules are often more sensitive than enzyme immunoassays, but require specialized instrumentation and often suffer from high background contamination resulting from intrinsic fluorescent and luminescent qualities of some proteins and light-scattering effects.
Pre- and post-test results show that parents significantly increased their knowledge antibiotics chart 150 mg roxithromycin amex, skills antibiotics for acne while pregnant purchase roxithromycin discount, comfort and confidence in communicating with their adolescents about sexuality and sexual risk reduction (Armistead et al antibiotic resistance cases buy roxithromycin mastercard, 2006; Miller et al antimicrobial stewardship program buy 150mg roxithromycin. However the impact of parent communication on actual levels of sexual violence against girls has not been directly assessed. The evaluation used a simple pre and post design and had no comparison group so further research is needed to test the findings. The programme was found to be effective in moderating negative attitudes and beliefs related to gender based and sexual violence and results indicated positive change in norms. Rates of intimate partner violence and non partner sexual violence were reduced and there was an increase in knowledge about rape and sources of help and support. Challenges to implementation identified from the programme were low levels of literacy in camps which made evaluation and information sharing difficult; the need to target women; to address rape related pregnancy; to stimulate demand for post rape care. It aims to prevent sexual abuse and exploitation by setting standards for the ethical behaviour of humanitarian workers and adopting a zerotolerance policy towards any form of abuse or violence. The code applies to all workers, including staff, volunteers, casual labourers, guards and senior managers, and lays out expectations for humanitarian workers and consequences for breaching the code (Levine and Bowden, 2002). One project was identified that sought to evaluate a Code of Conduct for Humanitarian Workers in Kenya that was developed in 2003. At the camp level, a reduction in reported cases of sexual abuse and exploitation was found after the campaign. There was also evidence of ownership of the project by refugees, who formed committees of youth, women and community leaders and who continued to peacekeepers and aid workers emerged and attracted media interest from 2001 onwards following reports into sexual abuse and exploitation in refugee communities 100 Ending Child Sexual Abuse and Exploitation: A Review of the Evidence Contents Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Section 9 References promote messages of prevention after the project ended (Xefina Consulting 2007). This evaluation provides some promising findings regarding the effectiveness of the Code, but importantly highlights the fact that drafting a code in and of itself is not enough. People must be aware of their rights and there must be pathways for complaints and reports to be made for a code to be effective. A review of effective field practice has highlighted, however, that these strategies may displace rather than prevent sexual violence (Anderson, 2010). Having good communication and trust between patrollers and camp members can increase effective prevention. Coordination, such as the establishment of joint protection teams that are teams of military and civilian personnel carrying out patrolling tasks, is recommended as crucial in sharing information about patterns of sexual violence in areas of conflict and crisis. Attention to camp design, layout, security and lighting, for instance, has been found to contribute to a safer environment for women and children in conflict settings. For displaced women and girls in some conflict-affected contexts, collecting firewood or water and visits to marketplaces/ trade routes puts them at particular risk of rape, abduction and murder. There has been a welcome widening of focus of primary prevention from strategies that target individual child risks to include the wider community and contextual factors. Three types of primary prevention strategies to tackle sexual abuse and exploitation were found: a) those aimed at mobilisation or education to raise awareness and change social norms, attitudes and behaviour; b) situational prevention; and c) prevention combining empowerment with reducing risks and vulnerabilities. It is likely that all three approaches are needed for an effective prevention approach. Primary prevention programmes specifically addressing child sexual abuse for pre-adolescent children are predominantly education based, teaching children about safe and unsafe touches and encouraging them to protect themselves by telling a trusted adult. Teaching self defense and empowerment skills may be more appropriate for adolescent girls at risk of sexual assaults from peers and boyfriends. Although plenty of prevention programmes on online safety for children exist, no robust studies were found to show effectiveness and impact. Evaluations of child sexual exploitation primary prevention strategies also appear to be limited. The distinction between online and offline child sexual abuse and exploitation is increasingly blurred although the online world can provide a safe environment for disinhibited opportunistic offenders.