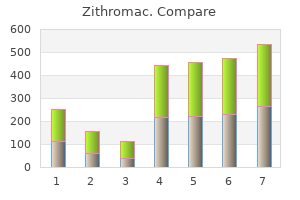
"Order zithromac without prescription, antibiotic resistance research paper".
By: Z. Jose, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
His medical history was clear apart from his having had rheumatic fever and hepatitis C in childhood antibiotic resistance hand sanitizer generic 100mg zithromac with mastercard. Case history 2 A 46-year-old schoolteacher noticed white thickening of the buccal mucosa after reading about oral leukoplakia on a health Website antibiotics for uti urinary tract infection purchase zithromac on line. He consulted his general dental practitioner who reassured him and referred him for specialist opinion treatment for gbs uti in pregnancy discount zithromac 100mg online. At the clinic antibiotics for urinary tract infection in dogs zithromac 250 mg fast delivery, the specialist found that there were white bands at the level of the occlusal plane on the buccal mucosa and noted marked wear facets on the teeth. If a biopsy of the buccal mucosa was taken, which features would you expect to be present? What factors should you take into account when taking a mucosal biopsy to aid the pathologist? Why are both swabs and smears taken for the diagnosis of suspected Candida infection? Sawtooth rete ridges are characteristic of lichen planus in skin biopsies and are found in less than one-third of oral biopsies. Striae may be conspicuous or evident on close examination of gingival lesions in desquamative gingivitis caused by lichen planus. It is found in pemphigus, some forms of mucous membrane pemphigoid and other vesiculo-bullous dermatoses. The antigenic targets are located in and around the hemidesmosome/basement membrane complex. It may also be caused by mucous membrane pemphigoid, pemphigus, plasma cell mucositis and allergic reactions. Perilesional mucosa is required for direct immunofluorescence and the tissue must be snap-frozen or submitted to the laboratory in special transport medium. The subepithelial infiltrate typically comprises mostly T lymphocytes and histiocytes. Topical corticosteroids are often used to treat symptomatic erosive lichen planus. In chronic hyperplastic candidiasis (candidal leukoplakia), pseudohyphae invade the parakeratin layer. Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder; it is one form of diffuse mucocutaneous candidiasis. Significant systemic absorption of miconazole may occur and has been reported to potentiate the action of warfarin, resulting in severe purpura. Acute leukaemia more typically results in enlargement of the gingivae, through infiltration by leukaemic cells. Excessive bleeding has been reported and such cases are best referred for specialist care. Testing for -gliadin antibody has been replaced by testing for endomysial or tissue transglutaminase antibody. A positive result should trigger referral to a gastroenterologist for further investigation. Aciclovir cream is not suitable for intraoral use; systemic aciclovir may be prescribed if necessary. Other very rare forms of hereditary white patch, such as those associated with tylosis and dyskeratosis congenita, are associated with malignancy. PeutzΊeghers is a syndrome of mucocutaneous melanotic pigmentation and gastrointestinal polyposis. Mucous membrane pemphigoid can affect the oral cavity, conjunctive and genital mucosa. Testing by indirect and direct immunofluorescence can be helpful in establishing the diagnosis. All such suspicious oral lesions should be biopsied or referred for consultant opinion. The most common underlying disease process is lichen planus, but vesiculo-bullous disorders can have similar clinical appearances. Plasma-cell mucositis is a rare condition that affects the oral mucosa and that can extend into the supraglottic larynx.
Interlock the fingers of your hands and with straight arms press down on the sternum 5Ͷ cm virus 268 purchase zithromac from india. In acquired cases antibiotics reduce bacterial biodiversity buy zithromac no prescription, treatment is that of the underlying cause and intravenous isoprenaline virus vs bacterial infection purchase zithromac 250mg amex. The patient is unconscious and apnoeic with absent arterial pulses (best felt in the carotid artery in the neck) virus back pain 250 mg zithromac. Irreversible brain damage occurs within 3 minutes if an adequate circulation is not established. Resuscitation is stopped when there is return of spontaneous circulation and a pulse, or further attempts at resuscitation are deemed futile. Post-resuscitation care centres on maintaining arterial oxygen saturation (948%), blood glucose values <10 mmol/L and therapeutic hypothermia. Prognosis In many patients resuscitation is unsuccessful, particularly in those who collapse out of hospital and are brought into hospital in an arrested state. In patients who are successfully resuscitated, the prognosis is often poor because they have severe underlying heart diseases. Studies suggest that therapeutic hypothermia (32ͳ4у for 12Ͳ4 hours) might improve neurological outcomes in unconscious adult patients with spontaneous circulation after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest due to ventricular fibrillation. It is a common condition, with an estimated annual incidence of 10% in patients over 65 years. The long-term outcome is poor and approximately 50% of patients are dead within 5 years. Aetiology Ischaemic heart disease is the most common cause in the developed world and hypertension is the most common cause in Africa (Table 10. Any factor that increases myocardial work (arrhythmias, anaemia, hyperthyroidism, pregnancy, obesity) may aggravate existing heart failure or initiate failure. Pathophysiology When the heart fails, compensatory mechanisms attempt to maintain cardiac output and peripheral perfusion. However, as heart failure progresses, the mechanisms are overwhelmed and become pathophysiological. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system Activation of the sympathetic nervous system improves ventricular function by increasing heart rate and myocardial contractility. Constriction of venous capacitance vessels redistributes flow centrally, and the increased venous return to the heart (preload) further augments ventricular function via the Starling mechanism. Sympathetic stimulation, however, also leads to arteriolar constriction; this increases the afterload, which eventually reduces cardiac output. ReninΡngiotensin system the fall in cardiac output and increased sympathetic tone lead to diminished renal perfusion, activation of the reninΡngiotensin system and hence increased fluid retention. Salt and water retention further increases venous pressure and maintains stroke volume by the Starling mechanism. As salt and water retention increases, however, peripheral and pulmonary congestion causes oedema and contributes to dyspnoea. In heart failure (y) the ventricular function curve is relatively flat, so that increasing the preload has only a small effect on cardiac output. The effect of their action may represent a beneficial, albeit inadequate, compensatory response leading to reduced cardiac load (preload and afterload). There is increasing interest in monitoring levels to help guide heart failure therapy. Ventricular dilatation Myocardial failure leads to a reduction of the volume of blood ejected with each heartbeat, and thus an increase in the volume of blood remaining after systole. Eventually the increased venous pressure contributes to the development of pulmonary and peripheral oedema. In addition, as ventricular diameter increases, greater tension is required in the myocardium to expel a given volume of blood, and oxygen requirements increase. Ventricular remodelling this is a process of hypertrophy, loss of myocytes and increased interstitial fibrosis which all contribute to progressive and irreversible pump (contractile) failure.
In overlap syndrome antimicrobial quizzes generic zithromac 500mg with amex, myositis appears together with another autoimmune disease antibiotic resistant pneumonia discount zithromac online. Peripheral Nerve and Muscle 345 Lid edema Neuromuscular Disorders pain induced by normally nonpainful stimuli and is explained by the sensitization of nociceptors by pain-related substances such as bradykinin antibiotics for acne bad order zithromac now, serotonin kinds of antibiotics for acne buy generic zithromac 500mg line, and prostaglandin. A "charleyhorse" is a type of myalgia that normally begins 8Ͳ4 hours after muscle overuse (simultaneous stretching and contraction) and lasts 5ͷ days. Myalgia can be triggered by disorders whose primary pathology lies anywhere in the nervous system (peripheral nerve, spinal cord, brain). Pressure or traction on a muscle causes myalgia that subsides once the mechanical stimulus is removed, while inflammatory and other lesions in muscle cause persistent and gradually increasing myalgia. Muscle ischemia and/or metabolic dysfunction are reflected by myalgia occurring only during muscle activity. Myalgia includes allodynia, which is defined as Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Causes of Myalgia Type of Myalgia Localized myalgia ܠHematoma ܠMyositis ܠIschemic ܠToxic-metabolic ܠOveractivity ܠExerciseinduced ܠParkinsonian ܠMuscle spasm ܠPain at rest Generalized myalgia ܠMyositis ܠToxic-metabolic ܠOther Selected Causes ܠTrauma, coagulopathy ܠInfectious: Streptococcal infection, trichinosis, influenza, epidemic pleurodynia. Noninfectious: Nodular focal myositis, eosinophilic fasciitis, sarcoidosis, myositis ossificans ܠArteriosclerosis (intermittent claudication), embolism ܠAcute alcoholic myopathy, metabolic myopathy (pp. Rhabdomyolysis Local or generalized damage to skeletal muscle can cause myoglobinuria and an elevated serum concentration of creatine kinase, usually accompanied by the acute onset of proximal or diffuse weakness, with myalgia, muscle swelling, and general manifestations including nausea, vomiting, headache, and sometimes fever. The creatine kinase level may be chronically elevated in susceptible individuals, who can be identified with an in vitro contracture test performed in specialized laboratories. Malignant neuroleptic syndrome can also be induced by abrupt withdrawal of dopaminergic agents in patients with Parkinson disease. Remarkably, paraneoplastic syndromes sometimes appear months or years before the underlying malignancy becomes clinically manifest. Paraneoplastic neuromuscular syndromes typically present with marked weakness of subacute onset. Toxic Neuromuscular Syndromes the muscle fiber lesions regress if the responsible substance is eliminated in timely fashion (Table 75, p. Myopathy in Endocrine Disorders Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, Cushing syndrome, steroid myopathy, and acromegaly all cause proximal weakness, while Addison disease and primary hyperaldosteronism usually cause generalized weakness. Timely correction of the endocrine disorder or withdrawal of steroid drugs is usually followed by improvement. It causes distal, symmetric weakness with prominent involvement of the muscles of respiration, resulting in prolonged ventilator dependence and delayed mobilization. Peripheral Nerve and Muscle 347 348 Rohkamm, Color Atlas of Neurology ɠ2004 Thieme All rights reserved. History and Physical Examination A detailed description of diagnostic evaluation procedures can be found in the textbooks listed on p. The goals of history-taking, physical examination, and additional testing (if necessary) are: ܠData collection (manifestations of disease) ܠLocalization of the lesion ܠProvision of an etiological diagnosis Data Collection the diagnostic process begins with the history and physical examination. The physician engages the patient in a structured conversation about the manifestations of the illness. The physician must remember that the patient is the "expert" in this situation, as the patient alone knows what is troubling him (though perhaps helpful information can also be obtained from a close relative or friend). The physician aims to obtain accurate information on the nature, location, duration, and intensity of the symptoms by listening patiently and asking directed questions in an atmosphere of openness and trust. Questionnaires, computer programs, and ancillary personnel cannot be used for primary history-taking, as they do not enable the construction of a trusting physicianΰatient relationship (though they may provide useful additional information at a later stage). The general and neurological physical examination may yield important clues to the disease process, but only if the examiner has the requisite knowledge of the underlying principles of (neuro-)anatomy, (neuro-)physiology, and (neuro-)pathology. The unselective, "shotgun" application of every possible technique of neurological examination in every patient is not only a waste of time and money; it generally only creates confusion rather than clarifying the search for the diagnosis. The neurological examination of small children, patients with personality changes or mental illness, and unconscious patients poses special challenges. Orientation (to person, place, and time), attention, concentration, memory, thought processes, language function, level of consciousness.
Order zithromac 250 mg visa. Chapter 12: Antibacterial Mechanisms of Action & Bacterial Resistance Mechanisms.
A number of methods can be used to compute the center of mass of an object using balancing techniques antibiotics for deep sinus infection buy 250 mg zithromac with mastercard. The most common is to compute the center of mass of individual segments m4sonic - virus buy discount zithromac 100mg online, which are then combined to provide the location of the center of mass of the total system virus war buy zithromac 500 mg free shipping. Two-dimensional coordinates from digitized data (x antibiotics for uti for pregnancy cheap zithromac express, y) and the previously mentioned properties of the segments are used to analyze one segment at a time and then calculate the total body center of mass. The estimation of the total body center of mass position is obtained by applying a model that assumes that the body is a set of rigid segments. The center of mass of the total body is calculated using the inertial parameters of each segment and its position. Before presenting the computations for this method, the source of the information concerning the body segments must be approached. They are measures based on cadaver studies, mathematical geometric modeling, and mass scanning. Several researchers have presented formulae that estimate the mass and the location of the center of mass of the various segments based on cadaver studies (8,9,10,36). These researchers have generated regression or prediction equations that make it possible to estimate the mass and the location of the center of mass. These predicted parameters are based on known parameters, such as the total body weight and the length or circumference of the segment. An example of a regression equation based on Clauser and colleagues (9) for estimating the segment mass of the leg is as follows: leg mass = 0. The location of the center of mass of the segment is usually presented as a percentage of the segment length from either the proximal or distal end of the segment. Other researchers have used mathematical geometric models to predict the segment masses and locations for the center of mass calculation. This has been done by representing the individual body segments as regular geometric solids (1,20,21,22). Regression equations based on the geometry of these solids require the input of several measurements for each segment. For example, the thigh segment requires measurement of the circumference of the upper and lower thigh, the length of the thigh, and the total body mass to estimate the desired parameters for the segment. The third method of determining the necessary segment characteristics is the gamma-scanning technique suggested by Zatsiorsky and Seluyanov (66). A measure of a gamma-radiation beam is made before and after it has passed through a segment. This allows calculation of the mass per unit surface area and thus generates prediction equations to determine the segment characteristics. The following example equation is based on these data and predicts the mass of the leg segment: y = -1. The following equation will predict the location of the center of mass along the longitudinal axis for the same segment: y = -6. All of these methods have been used in the literature to determine the segment characteristics of the center of mass, and all give reasonable estimates of these parameters. In a typical biomechanical analysis, researchers collect height and weight measurements, collect position data on the segmental end points, and calculate the location of the center of mass and the proportionate weight of the segment using information provided by studies in the literature. Tables 11-3 and 11-4 present estimates of the center of mass location and proportionate weights generated from four studies (8,9,10,41). The thigh segment at toe-off (frame 76) from Appendix B will be used as an example to calculate these parameters. The location of the center of mass in the x- or horizontal direction would be: ta b L e 11-3 Center of Mass Location: Percent of Segment Length from Proximal End Plagenhoef et al. Similarly, for the y- or vertical direction: ycm = yp - [length of the segment in the y-direction נ0. The center of mass must be between the values for the proximal and distal ends of the segments. This procedure must be carried out for each segment using the coordinates of the joint centers to define the segments. Location of the center of mass in a three-point mass appears in every term in the equation, it can be removed from the equation, resulting in: m1x1 + m2x2 + m3x3 = Mxcm After substitution of the values from Figure 11-20 into this equation, only one quantity is unknown, xcm.
Growth factor binding results in dimerization of these receptors and consequent activation of the tyrosine kinase domain treatment for dogs eating grapes order 100 mg zithromac. Phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the receptor itself generates binding sites for signalling proteins which initiate complex cascades of biochemical events resulting in changes in gene expression virus encyclopedia order generic zithromac from india, cell proliferation and prevention of apoptosis infection knee replacement symptoms buy 500 mg zithromac amex. The cell cycle the cell division cycle antibiotics with food order zithromac 250mg on-line, generally known simply as the cell cycle, is a complex process that lies at the heart of haemopoiesis. Dysregulation of cell proliferation is also the key to the development of malignant disease. The duration of the cell cycle is variable between different tissues but the basic principles remain constant. The cycle is divided into the mitotic phase (M phase), during which the cell physically divides, and interphase during which the chromosomes are duplicated and cell growth occurs prior to division. The M phase is further partitioned into classical mitosis in which nuclear division is accomplished, and cytokinesis in which cell fission occurs. If cells rest prior to division they enter a G0 state where they can remain for long periods of time. Chapter 1 Haemopoiesis / 11 M phase M Cdk2 Cyclin B G2 G1 G0 Cdk2 Cyclin E Cyclin A which phosophorylate downstream protein targets and cyclins which bind to Cdks and regulate their activity. An example of the importance of these systems is demonstrated by mantle cell lymphoma which results from the constitutive activation of cyclin D1 as a result of a chromosomal translocation (see p. S Cdk2 Apoptosis Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is a regulated process of physiological cell death in which individual cells are triggered to activate intracellular proteins that lead to the death of the cell. It is an important process for maintaining tissue homeostasis in haemopoiesis and lymphocyte development. Following death, apoptotic cells display molecules that lead to their ingestion by macrophages. Progression through cell cycle is regulated by specific combinations of cyclin-dependent protein kinases (Cdk) and cyclin proteins. The synthesis and degradation of different cyclins stimulates the cell to pass through the different phases of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is controlled by two checkpoints which act as brakes to coordinate the division process at the end of the G1 and G2 phases. Cytochrome c binds to the cytoplasmic protein Apaf-1 leading to activation of caspases. Many of the genetic changes associated with malignant disease lead to a reduced rate of apoptosis and hence prolonged cell survival. Apoptosis is the normal fate for most B cells undergoing selection in the lymphoid germinal centres. Several translocations leading to the generation of fusion proteins such as t(9; 22), t(1; 14) and t(15; 17) also result in inhibition of apoptosis (see Chapter 11). Necrosis is death of cells and adjacent cells due to ischemia, chemical trauma or hyperthermia. There is usually an inflammatory infiltrate in response to spillage of cell contents. It may be involved in cell death but in some situations also in maintaining cell survival by recycling nutrients. Transcription factors Transcription factors regulate gene expression by controlling the transcription of specific genes or gene families. Mutation, deletion or translocation of transcription factors underlie many cases of haematological neoplasms. The adhesion molecules are thus important in the development and maintenance of inflammatory and immune responses, and in plateletζessel wall and leucocyteζessel wall interactions. Expression of adhesion molecules can be modifed by extracellular and intracellular factors and this alteration of expression may be quantitative or functional. The pattern of expression of adhesion molecules on tumour cells may determine their mode of spread and tissue localization. The adhesion molecules may also determine whether or not cells circulate in the bloodstream or remain fixed in tissues. Adhesion molecules A large family of glycoprotein molecules termed adhesion molecules mediate the attachment of marrow precursors, leucocytes and platelets to various components of the extracellular matrix, to endothelium, to other surfaces and to each other. The adhesion molecules on the surface of leucocytes are termed receptors and these interact with molecules (termed ligands) on the surface of potential target cells. Three main families exist: Haemopoiesis (blood cell formation) arises from pluripotent stem cells in the bone marrow.